NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science
Chapter 2 (Is Matter Around Us Pure)
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure: Here in this post we are giving NCERT solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2. This solution contains questions, answers, images, step by step explanations of the complete Chapter 2 titled Is Matter Around Us Pure of Science taught in class 9 and some additional important very short answer, short answer and long answer questions and answers for better preparation of the chapter 2 NCERT Class 9 Science. If you are a class 9 student and using NCERT Textbook to study Science and studied chapter -2 then you may need chapter 2 solutions for your preparation. So, In this article you will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure.
Questions inside the Chapter- 2 Is Matter Around Us Pure
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter-2
Page 15
Question 1:
What is meant by a pure substance?
Answer :
A pure substance is the one that consists of a single type of particles, i.e., all constituent particles of the substance have the same chemical nature. Pure substances can be classified as elements or compounds.
Question 2:
List the points of differences between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures.
Answer:
A homogeneous mixture is the mixture having a uniform composition throughout the mixture. For example: salt in water, sugar in water, copper sulphate in water.
A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture having a non-uniform composition throughout the mixture.
For example: oil and water, sodium chloride and iron fillings, salt and
sulphur.
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter-2
Page- 18
Question 1:
Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures with examples.
Answer :
A homogeneous mixture is a mixture having a uniform composition throughout the mixture. For example, mixtures of salt in water, sugar in water, copper sulphate in water, iodine in alcohol, alloy, and air have uniform compositions
throughout the mixtures. On the other hand, a heterogeneous mixture is a mixture having a non-uniform
composition throughout the mixture. For example, composition of mixtures of sodium chloride and iron fillings, salt and sulphur, oil and water, chalk powder in water, wheat flour in water, milk and water are not uniform throughout the mixtures.
Question 2:
How are sol, solution and suspension different from each other?
Answer :

Sol(Colloidal Solution): Example- milk of magnesia, mud
Solution : Example- salt in water, sugar in water, iodine in alcohol, alloy
Suspensions: Example- chalk powder and water, wheat flour and water
Question 3:
To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of
water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Answer :
Mass of solute (sodium chloride) = 36 g (Given)
Mass of solvent (water) = 100 g (Given)
Then, mass of solution = Mass of solute + Mass of solvent
= (36 + 100) g
= 136 g
Therefore, concentration (mass by mass percentage) of the solution
=
𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒
𝑀𝑎𝑠𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡
× 100 %
=
36
136
× 100 %
= 26.4 %
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter-2
Page 24
Question 1:
How will you separate a mixture containing kerosene and petrol (difference in their boiling points is more than 25°C), which are miscible with each other?
Answer :
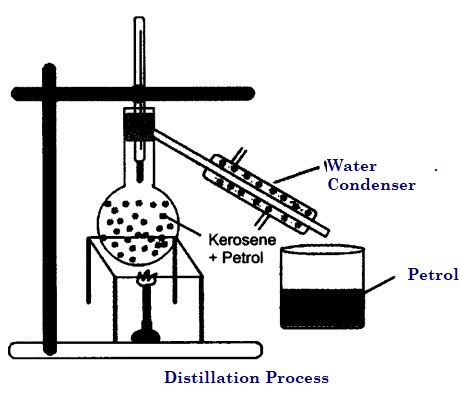
A mixture of two miscible liquids having a difference in their boiling points more than 25°C can be separated by the method of distillation. Therefor, kerosene and petrol can be separated by distillation.
In this method, the mixture of kerosene and petrol is taken in a distillation flask and a thermometer fitted in it. We also need a beaker, a water condenser, and a Bunsen burner. The apparatus is arranged as shown in the above figure. Then, the mixture is heated slowly. The thermometer should be watched continuously. Petrol will vaporize first as it has lower boiling point. It condenses in the condenser. The condensed Petrol is collected from the condenser outlet, whereas Kerosene is left behind in the distillation flask.
Question 2:
Name the technique to separate
(i) butter from curd
(ii) salt from sea-water
(iii) camphor from salt.
Answer :
(i) Butter can be separated from curd by centrifugation.
(ii) Salt can be separated from sea-water by evaporation.
(iii) Camphor can be separated from salt by sublimation.
Question 3.
What types of mixtures can be separated by technique known as crystallisation ?
Answer:
The solid mixtures in which one component or impurity is less soluble in a particular solvent as compared to the other. For example, impure samples of copper sulphate, potassium nitrate, potash alum etc. can be purified by this method.
Question 4.
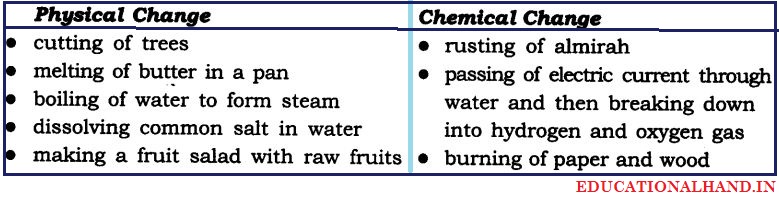
Classify the following into physical and chemical changes.
- Cutting of trees
- Melting of butter in a pan
- Rusting of almirah
- Boiling of water to form steam
- Passing of electric current through water and the water breaking down into hydrogen and oxygen gases
- Dissolving common salt in water
- Making of fruit salads with raw fruits
- Burning of paper and wood.
Answer:
Physical change : A change which can be easily reversed is a physical change.
Chemical change: A change which cannot be reversed is a chemical change in nature.
Based on this concept, the changes that are listed may be classified as :
Question 4.
Try to segregate the things around you as pure substances and mixtures :
(a) distilled water
(b) curd
(c) diamond
(d) ice cream
(e) kerosene
(f) cooking oil
(g) steel
(h) graphite
(i) raw rubber
(j) solder wire.
Answer:
Pure substances : Distilled water, diamond, graphite, raw rubber
Mixtures : curd, ice cream, kerosene oil, cooking oil, steel, solder wire (alloy of lead and tin)
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter-2
EXERCISE
Question 1.
Which separation techniques will you apply for the separation of the following ?
- Sodium chloride from its solution in water. (CBSE 2012)
- Ammonium chloride from a mixture containing sodium chloride and ammonium chloride.
- Small pieces of metal in the engine oil of a car. (CBSE 2012, 2013, 2014)
- Different pigments from an extract of flower petals.
- Butter from curd.
- Oil from water. (CBSE 2012, 2013)
- Tea leaves from tea.
- Iron pins from sand.
- Wheat grains from husk. (CBSE 2012)
- Fine mud particles suspended in water. (CBSE 2012, 2013)
Answer:
- Evaporation : Water will evaporate leaving behind sodium chloride.
- Sublimation : Ammonium chloride will be collected as sublimate.
- Filtration : Pieces of metal can be separated by filtration.
- Chromatography : Pigments (colored components) from the extract of flower plants can be separated by chromatography.
- Centrifugation : Butter will get separated upon centrifugation.
- Separating funnel : Oil and water can be separated by the use of separating funnel.
- Filtration : Upon filtration through a sieve, tea leaves will be collected on the sieve.
- Magnetic separation : A magnet will attract iron pins and not sand particles.
- Sieving : Wheat grains from husk can be separated with the help of sieve.
- Sedimentation : As a result of sedimentation, mud particles will settle as precipitate. It can be separated later on by filtration.
Question 2.
Write the steps you would use for making tea. Use the words-solution, solvent, solute, dissolve, soluble, insoluble, filtrate and residue.
Answer:
Tea can be made in the steps given bellow:
- Take approximately two to three cups of water (solvent) in a pan and heat it on a gas burner.
- When water starts boiling, add some amount of milk and sugar (both are solutes).
- Now, stir with a spoon. As a result, sugar will dissolve and milk will become miscible with water. A solution will be formed.
- Further boil the solution for sometime so that sugar may completely dissolve.
- Now add the required amount of tea leaves (solute) to the pan. Boil again and filter through a sieve. Tea will be collected as filtrate. Tea leaves will get collected on sieve as residue.
Question 3.
Pragya tested the solubility of four different substances at different temperatures and collected the data as given below (results are given in the following table, as grams of substance dissolved in 100 grams of water to form a saturated solution).
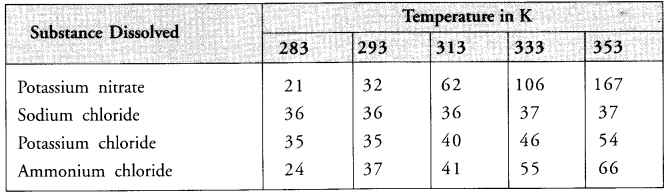
(a) What mass of potassium nitrate would be needed to produce a saturated solution of potassium nitrate in 30 grams of water at 313 K ?
(b) Pragya makes a saturated solution of potassium chloride in water at 353 K and leaves the solution to cool at room temperature. What would she observe as the solution cools ? Explain.
(c) Find the solubility of each salt at 293 K. Which salt has the maximum solubility at this temperature ?
(d) What is the effect of change of temperature on the solubility of a salt ?
Answer:
(a) At-313 K, in the saturated solution
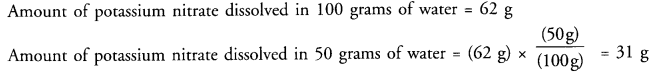
(b) When the saturated solution prepared at 353 K is cooled to room temperature (about 298 K) the solubility of potassium chloride in water will decrease. It will slowly start separating as a crystalline white residue at the bottom of the container.
(c) The solubility of the salt in a water is defined as :
the maximum amount of the salt which is dissolved in 100 g of water (or any other solvent) to form a saturated solution at a given temperature
In the light of this, at 293 K

(d) With rise in temperature, the solubility of all the salts in water increases. This has been shown by the data given in the table. Similarly, when the temperature is decreased, the solubility of these salts in water decreases.
Question 4.
Explain the following, giving examples :
(a) Saturated solution
(b) Pure substance
(c) Colloid
(d) Suspension.
Answer:
(a) Saturated solution: A solution becomes saturated if the solute starts separating at the bottom of the container in which the solution is being prepared at a given temperature. A saturated solution generally becomes unsaturated upon heating.
(b) Pure substance: A pure substance means a single substance (or matter) which cannot be separated into other kinds of matter by any physical process.
(c) Colloid: Colloidal solutions are also heterogeneous in nature like suspensions, but they have smaller size of the particles which are distributed. It ranges between 1 nm to 100 nm i.e., in between the particle size of true solution and suspension.
(d) Suspension: A suspension may be defined as a heterogeneous mixture in which the solid particles are spread throughout the liquid without dissolving in it. They settle as precipitate if the suspension is left undisturbed for sometime.
Question 5.
Classify each of the following as a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture :
(a) Soda water
(b) Wood
(c) Air
(d) Soil
(e) Vinegar
(f) Filtered tea.
Answer:
Homogeneous mixture : Soda water, air, vinegar, filtered tea.
Heterogeneous mixture : Wood, soil.
Air is a homogeneous mixture of different gases. However, if some dust or other particles are present, then air becomes a heterogeneous mixture.
Question 6.
How would you confirm that the colourless liquid given to you is pure water ?
Answer:
This can be confirmed by the following experiments :
- Filter the colourless liquid through a very fine filter paper. If no residue is left on the filter paper, this means that the liquid is pure water and has no suspended inpurities present in it.
- Evaporate the colourless liquid in a china dish or beaker. In case no residue is left, this means that it is pure water and has no dissolved impurities present in it.
- Determine the boiling point of pure liquid. If it comes out to be nearly 373 K (100°C), this means that the pure liquid is water.
Question 7.
Which of the following materials fall in the category of pure substances ?
(a) Ice
(b) Milk
(c) Iron
(d) Hydrochloric acid
(e) Calcium oxide
(f) Mercury
(g) Brick
(h) Wood
(i) Air.
Answer:
Pure substances in the given list of materials are :
(a) Ice (compound)
(c) Iron (element)
(e) Calcium oxide (compound)
(f) Mercury (element).
Both milk and Hydrochloric acid are homogeneous mixtures. Please note that the acid is formed when the vapours of Hydrogen Chloride gas are passed through water.
Wood and air (containing suspended particles) are heterogeneous mixtures. However, air free from any suspended particles is a homogeneous mixture.
Question 8.
Identify the solutions among the following mixtures :
(a) Soil
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(d) Coal
(e) Soda water.
Answer:
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more non-reacting substances present in a single phase.
The Solutions among the above are :
(b) Sea water
(c) Air
(e) Soda water.
Question 9.
Which of the following will show “Tyndall effect” ?
- Salt solution
- Milk
- Copper sulphate solution
- Starch sol.
Answer:
Tyndall effect is shown by colloidal sol.
Because milk and starch sol are colloidal sol therefore, these will show Tyndall effect.
Question 10.
Classify the following into elements, compounds and mixtures :
- Sodium
- Soil
- Sugar solution
- Silver
- Calcium carbonate
- Tin
- Silicon
- Coal
- Air
- Soap
- Methane
- Carbon dioxide
- Blood.
Answer:
Elements : Sodium, Silver, Tin, Silicon.
Compounds : Calcium carbonate, Methane, Carbon dioxide.
Mixtures : Soil, Sugar solution, Coal, Air, Blood, Soap.
Question 11.
Which of the following are chemical changes ?
- Growth of a plant
- Rusting of iron
- Mixing of iron filings and sand
- Cooking of food
- Digestion of food
- Freezing of water
- Burning of a candle.
Answer:
Chemical changes among the above are :Growth of a plant, Rusting of iron, Cooking of food, Digestion of food, Burning of a candle.
