NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science
Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules – Here are all the questions answers for Class 9 Science Chapter 3. If you are a student of class 9 who is using NCERT Textbook to study Science, then you should go through Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules. After studying the lesson, if you are looking for answers of its questions. Then here is the solutions. You will get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules here.
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Topics and Sub Topics covered in Class: 9 Science Chapter: 3 Atoms and Molecules:-
- Atoms and Molecules
- Laws of Chemical Combination
- What is an Atom?
- What is a Molecule?
- Writing Chemical Formulae
- Molecular Mass and Mole Concept
These questions answers are the part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. Here we have given Class 9 NCERT Science Text book Solutions for Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules.
IN-TEXT QUESTIONS SOLVED
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page No. 32
Q1. In a reaction 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass carbonate.
Ans:


CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 3 IN-TEXT QUESTIONS SOLVED
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook Page 32
Q1. In a reaction 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium etkanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass carbonate.
Ans:

Q2. Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1 : 8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
Ans: Ratio of H : O by mass in water is:
Hydrogen : Oxygen —> H2O
∴ 1 : 8 = 3 : x
x = 8 x 3
x = 24 g
∴ 24 g of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas.
Q3. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
Ans: The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory that is the result of the law of conservation of mass is—the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound. Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Q4. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
Ans: The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook Page 35
Q1. Define the atomic mass unit.
Ans: One atomic mass unit is equal to one-twelfth (1/12th) of the mass of one atom of carbon-12 (C-12). The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12.
Q2. Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
Ans: Atom is too small to be seen with naked eyes. It is measured in nanometers.
1 m = 1000000000 nm
NCERT Textbook Questions – Page 39
Question 1. Write down the formulae of
(i) Sodium oxide
(ii) Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium sulphide
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide
Ans: The formula are

Q2. What is meant by the term chemical formula?
Ans: The chemical formula of the compound is a symbolic representation of its composition, e.g., chemical formula of sodium chloride is NaCl.
Q3. How many atoms are present in a
(i) H2S molecule and
(ii) P043- ion?
Ans:
(i) H2S —> Total 3 atoms are present
(ii) P043- —> Total 5 atoms are present
NCERT Textbook Questions – Page 40
Q1. Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, C02, CH4, C2H2,NH3, CH3OH.
Ans: The molecular mass are following:
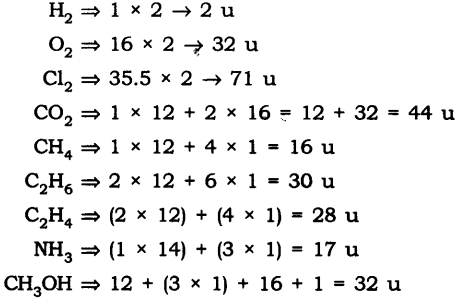
Q2.Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2C03, given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
Ans: The formula unit mass are following:
(i) ZnO = 65 u + 16 u = 81 u
(ii) Na2O = (23 u x 2) + 16 u = 46 u + 16 u = 62 u
(iii) K2C03 = (39 u x 2) + 12 u + 16 u x 3
= 78 u + 12 u + 48 u = 138 u
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook Page 42
Q1. If one mole of carbon atoms weigh 12 grams, what is the mass (in grams) of 1 atom of carbon?
Ans:
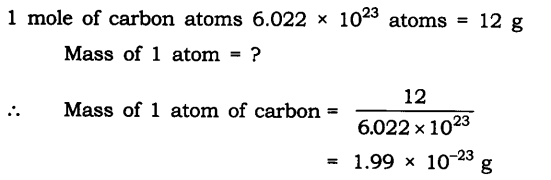
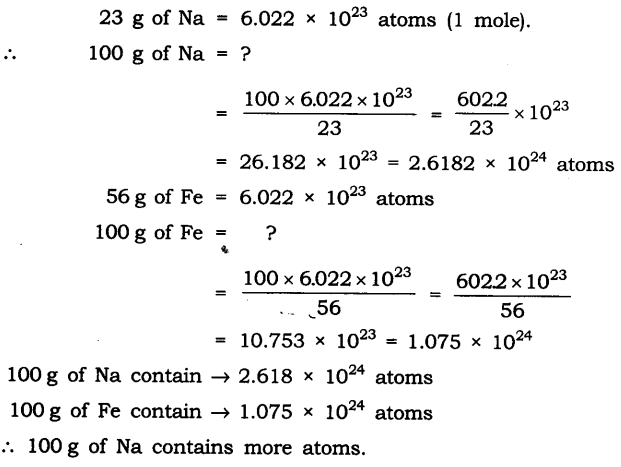
Q2. Which has more number of atoms, 100 grams of sodium or 100 grams of iron (given atomic mass of Na = 23 u, Fe = 56 u)?
Ans:
Questions From NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science
Q1. A 0.24 g sample of compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Ans: Boron and oxygen compound —> Boron + Oxygen
0.24 g —> 0.096 g + 0.144 g
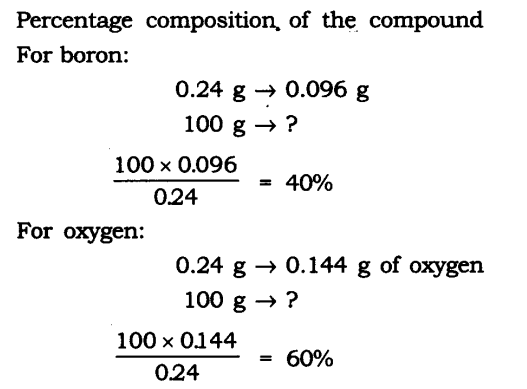
Q2. When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
Ans: The reaction of burning of carbon in oxygen may be written as:
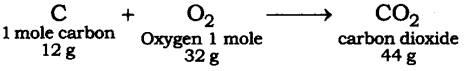
It shows that 12 g of carbon burns in 32 g of oxygen to form 44 g of Carbon Dioxide. Given that, 3 g of carbon reacts with 8 g of oxygen to form 11 g of carbon dioxide. It is given that 3.0 g of carbon is burnt with 8 g of oxygen to produce 11.0 g of CO2. Consequently 11.0 g of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.0 g of C is burnt in 50 g of oxygen consuming 8 g of oxygen, leaving behind 50 – 8 = 42 g of O2.
so, The answer governs the law of constant proportion.
Q3. What are poly atomic ions? Give examples.
Ans: The ions which contain more than one atoms (same kind or may be of different kind) and behave as a single unit are called polyatomic ions example: OH–, SO42-, CO32-.
Q4. Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate.
Ans:
(a) Magnesium chloride
Symbol —> Mg Cl
Change —> +2 -1
Formula —> MgCl2
(b) Calcium oxide
Symbol —> Ca O
Charge —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaO
(c) Copper nitrate
Symbol —> Cu NO
Change +2 -1
Formula -4 CU(N03)2
(d) Aluminium chloride
Symbol —> Al Cl
Change —> +3 -1
Formula —> AlCl3
(d) Calcium carbonate
Symbol —> Ca CO3
Change —> +2 -2
Formula —> CaC03
Q5. Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(a) Quick lime
(b) Hydrogen bromide
(c) Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulphate.
Ans:
(a) Quick lime —> Calcium oxide
Elements —> Calcium and oxygen
(b) Hydrogen bromide
Elements —> Hydrogen and bromine
(c) Baking powder —> Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Elements —> Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen
(d) Potassium sulphate
Elements —> Potassium, sulphur and oxygen
Q6. Calculate the molar mass of the following substances.
(a) Ethyne, C2H2
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 (Atomic mass of phosphorus = 31)
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e) Nitric acid, HNO3
Ans: The molar mass of the following are as: [Unit is ‘g’]
(a) Ethyne, C2H2 = 2 x 12 + 2 x 1 = 24 + 2 = 26 g
(b) Sulphur molecule, S8 = 8 x 32 = 256 g
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4=4 x 31 = i24g
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl = 1 x 1 + 1 x 35.5 = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5 g
(e) Nitric acid, HN03 = 1 x 1 + 1 x 14 + 3 x 16 = 1 + 14 + 48 = 63 g
Q7. What is the mass of
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms?
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms (Atomic mass of aluminium = 27)?
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2S03)?
Ans:
(a) Mass of 1 mole of nitrogen atoms = 14 g
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms
Mass of 1 mole of aluminium atoms = 27 g
∴ Mass of 4 moles of aluminium atoms = 27 x 4 = 108 g
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3)
Mass of 1 mole of Na2SO3 = 2 x 23 + 32 + 3 x 16 = 46 + 32 + 48 = 126 g
∴ Mass of 10 moles of Na2SO3 = 126 x 10 = 1260 g
Q8. Convert into mole.
(a) 12 g of oxygen gas
(b) 20 g of water
(c) 22 g of Carbon dioxide.
Ans: (a) Given mass of oxygen gas = 12 g
Molar mass of oxygen gas (O2) = 32 g
Mole of oxygen gas 12/32 = 0.375 mole
(b) Given mass of water = 20 g
Molar mass of water (H2O) = (2 x 1) + 16 = 18 g
Mole of water = 20/18 = 1.12 mole
(c) Given mass of Carbon dioxide = 22 g
Molar mass of carbon dioxide (CO2) = (1 x 12) + (2 x 16)
= 12 + 32 = 44 g
∴ Mole of carbon dioxide = 22/44 = 0.5 mole
Q9. What is the mass of:
(a) 0.2 mole of oxygen atoms?
(b) 0.5 mole of water molecules?
Ans: (a) Mole of Oxygen atoms = 0.2 mole
Molar mass of oxygen atoms = 16 g
Mass of oxygen atoms = 16 x 0.2 = 3.2 g
(b) Mole of water molecule = 0.5 mole
Molar mass of water molecules = 2 x 1 + 16= 18 g .
Mass of H2O = 18 x 0.5 = 9 g
Q10. Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 16 g of solid sulphur.
Ans: Molar mass of S8 sulphur = 256 g = 6.022 x 1023 molecule
Given mass of sulphur = 16 g
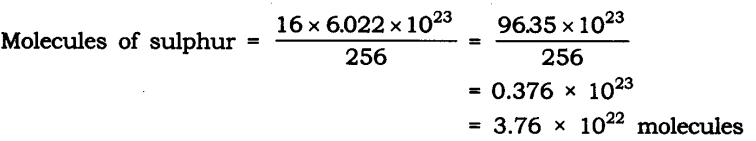
Q11. Calculate the number of aluminium ions present in 0.051 g of aluminium oxide. (Hint: The mass of an ion is the same as that of an atom of the same element. Atomic mass of Al = 27 u)
Ans: Molar mass of aluminium oxide Al203
= (2 x 27) + (3 x 16)
= 54 + 48 = 102 g.

