NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 2
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter-2
Some Important Questions Answers
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter-2 Some Important Questions Answers: Here we are giving some important question based on NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter-2 Is Matter Around Us Pure . If you have studied NCERT Class 9 Science chapter 2 then it will help you to prepare this chapter-2 in better way.
Some Important Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
A shining thick liquid is often used in glass thermometers. Name it.
Answer:
The shining liquid is mercury. It is used in glass thermometers as it does not stick to glass.
Question 2.
Name two metals which are both malleable and ductile.
Answer:
Copper and silver are both malleable and ductile.
Question 3.
A diamond knife is quite often used for cutting glass. Why ?
Answer:
Diamond is probably the hardest substance known. Therefore, a knife made from a special type of diamond is used for cutting glass.
Question 4.
Flow will check the purity of a pure chemical compound in the solid state ?
Answer:
The purity of a pure chemical compound can be checked by finding its melting point experimentally and by comparing it with its standard melting point value available in the form of tables. In case, the two values are nearly the same, the substance is pure. Otherwise, it is not.
Question 5.
A hard substance when bent produces a tinkling sound. Predict its nature.
Answer:
The hard substance is a metal. Actually metals are sonorous and produce tinkling sound when bent.
Question 6.
Give one test to show that brass is a mixture and not a compound.
Answer:
When we try to melt brass, it does not have a sharp melting point. This shows that it is not a compound. It is a homogeneous mixture of copper and zinc and is called alloy.
Question 7.
To the already prepared solution of a solute A’ prepared in water, a small amount of A is added. However, it does not dissolve. What does it indicate ?
Answer:
This indicates that the solution of the substance A in water is of saturated nature. It is called saturated solution.
Question 8.
What is the range of the size of the particles of dispersed phase in a colloidal solution ?
Answer:
It ranges from 1 nm (10~9 m) to 100 nm (10~7 m).
Question 9.
When a beam of light was passed through the solution of a substance A dissolved in water, the path of light could be seen. Predict the nature of the solution.
Answer:
The solution of substance A in water is colloidal solution. The colloidal particles scattered the light when it was passed through the solution due to Tyndall effect.
Question 10.
What will happen if a colloidal solution of sulphur is centrifuged in a centrifugal machine for sometime.
Answer:
The yellow precipitate of sulphur will settle at the bottom of the tube and the solution collected above the precipitate will be colorless.
Question 11.
How will you justify that rusting of iron is a chemical change ?
Answer:
The rust is a brown chemical compound known as hydrated ferric oxide (Fe2O3.xH2O). It can not be removed from the surface of the metal by any means. Formula of rust shows that iron has undergone a chemical change.
Question 12.
Why do not the dispersed phase particles in a colloidal solution combine with one other ?
Answer:
They donot come closer because of the presence of either positive or negative charge on them. Due to mutual repulsion, these particles remain scattered in a colloidal solution.
Question 13.
What are the units of mass percent ?
Answer:
Mass percent has no units as it is simply a ratio.
Question 14.
What is the nature the solution formed by mixing mustard oil and water ?
Answer:
It is a colloidal solution known as emulsion.
Question 15.
Give one example of the colloidal solution in which solid acts as the dispersed phase and gas as the dispersion medium.
Answer:
Dust storm in which solid particles are dispersed in air.
Question 16.
Name two compounds which sublime on heating.
Answer:
Ammonium chloride and iodine crystals.
Question 17.
You are provided with a mixture of carbon tetrachloride and water. How will you separate the constituents ?
Answer:
Both are immiscible liquids. The separation can be done by the use of a separating funnel.
Question 18.
Give one example of
(a) solution of a gas in a liquid
(b) solution of number of gases.
Answer:
(a) An aqueous solution of ammonia
(b) Air.
Question 19.
What is disperssed phase and dispersion medium in a colloid ?
Answer:
If a colloidal solution is compared to an ordinary solution, then dispersed phase is comparable to the solute and dispersion medium to the solvent.
Chapter 2 Science Class 9
Some Important Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What happens when a saturated solution of sodium chloride prepared at 60°C is allowed to cool at room temperature ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
A small amount of the salt gets separated at the bottom of the container as a residue.
Question 2.
Can a mixture of alcohol and water be separated with the help of a separating funnel ?
Answer:
No, it is not possible because alcohol (ethyl alcohol) and water are completely miscible. They do not form separate layers. Therefore, their separation cannot be done with the help of a separating funnel.
Question 3.
Sodium chloride contains two elements, but it is still a pure substance. Assign reason.
Answer:
The two elements sodium and chlorine have combined with each other by chemical reaction to form sodium chloride (NaCl) which is a chemical compound. Since these elements cannot be separated from each other by any physical process, sodium chloride is a pure substance.
Question 4.
What types of mixtures are represented by the following ?
(a) Carbon dioxide gas dissolved in water.
(b) Air containing suspended particles.
(c) Soap bubbles formed by blowing air into soap solution.
Answer:
(a) homogeneous
(b) heterogeneous
(c) heterogeneous.
Question 5.
Two miscible liquids A and B are present in a solution. The boiling point of A is 60°C while that of B is 90°C. Suggest a method to separate them.
Answer:
The separation can be done by the process of simple distillation. The vapours of the liquid A will rise in the flask when heated to a temperature of 60°C. They will pass through the condenser and will collect as “ distillate. The liquid B with higher boiling point will remain in the flask.
Question 6.
Classify the following as homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures :
- Copper sulphate solution
- A suspension of chalk in water
- Dust storm
- A dilute solution of alcohol in water.
Answer:
- homogeneous
- heterogeneous
- heterogeneous
- homogeneous.
Question 7.
Solubility of KNO3 at 313 K is 62 g. What mass of KNO3 would be needed to produce a saturated solution of KNO3 in 50 g of water at 313 K ?
Answer:
By definition of a saturated solution.
100 g of water at 313 K contain KNO3 = 62 g 50 g of water at 313 K contain KNO3 = 31 g
Question 8.
(a) State one property in which a solution of sugar in water resembles a mixture of sugar and sand and one property in which it differs from it.
(b) You are given two liquids; one a solution and the other a compound. How will you distinguish the solution from the compound ?
Answer:
(a) Resemblance : Both of them taste sweet due to the presence of sugar.
Difference : The constituent particles cannot be seen in the mixture of sugar and water but they can be easily seen in the mixture of sugar and sand.
(b) Try to separate the constituents present in both by some suitable physical method. Separation is possible in case of a solution but not in a compound.
Question 9.
What would you observe when :
(a) A saturated solution of potassium nitrate prepared at 60°C is allowed to cool to room temperature ?
(b) A mixture of iron filings and sulphur is heated strongly ?
(c) A colloidal solution of starch is passed through an ordinary filter paper ?
Answer:
(a) Crystals of potassium nitrate which are needle shaped would slowly appear at the bottom of the container which may be a china dish or a beaker.
(b) A greyish-black mass passes formed.
(c) The solution passes through the ordinary filter paper without leaving any residue.
Question 10.
The teacher instructed three students A, B and C respectively to prepare a 50% (mass by volume) solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH). A dissolved. 50 g of NaOH in 100 mL of water. B dissolved 50 g of NaOH in 100 g of water. The student C dissolved 50 g of NaOH in water to make 100 mL of solution. Which one of them has made the desired solution and why ? (CBSE 2014)
Volume of water = (250 – 150) = 100 mL
Answer:
The student ‘C’ has made the desired solution.
![]()
Question 11.
Point out whether the following statements are true or false :
- Particles in a colloidal solution can always be seen by naked eyes.
- Scattering of light occurs when a beam of liquid is passed through aqueous sugar solution.
- Colloidal solutions are of heterogeneous nature.
- Digestion of food is a chemical change.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True.
Question 12.
Calculate the mass of potassium sulphate required to prepare its 10 percent (mass percent) solution in 100 g of water.
Answer:
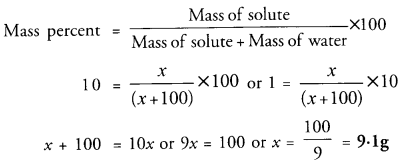
Question 13.
What volumes of ethyl alcohol and water must be mixed together to prepare 250 mL of 60 percent volume by volume solution of alcohol in water ?
Answer:
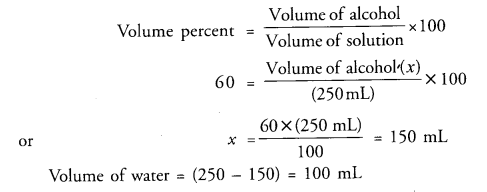
Question 14.
(a) Two students Ramesh and Alka were required to prepare 10 percent (mass/mass) solution of sodium chloride in water. For that, Ramesh dissolved 10 g of the salt in 100 g of water while Alka dissolved 10 g of the salt in 100 g of the solution. Which out of the two prepared the correct solution ?
(b) You are given a solution of a substance ‘A’. How will you test whether it is saturated or unsaturated with respect to A at a given temperature ?
Answer:
(a) Alka prepared the correct solution because by definition 10 percent solution of a substance means a solution containing 10 g of the solute dissolved in 100 g of it. This means that the mass of water in the solution is 90 g.
(b) Take the given solution in a beaker. Now add small amount of A to this solution and stir with a glass rod. If it dissolves in this solution, this means that the solution is unsaturated. If it does not dissolve and separates as a solid at the bottom of the beaker, the solution is saturated in nature.
Question 15.
What are solute and solvent in aereated drinks ?
Answer:
In aerated drinks, carbon dioxide (solute) is dissolved in water (solvent). It is infact, a homogeneous mixture.
Question 16.
How much water should be mixed with 12 mL of alcohol so as to obtain 12% alcohol solution ?
Volume of solute (alcohol)
Answer:

Question 17.
(a) All mixtures are homogeneous. Is this statement correct ? Justify your answer.
(b) How can a saturated solution be made unsaturated ?
Answer:
(a) No, this statement is wrong. Mixtures can be homogeneous only if the constituents present are uniformly mixed and there is no boundary of separation of these constituents.
A mixture is said to be heterogeneous if it does not have a uniform composition and also has visible boundaries of separation between the constituents.
A few examples of heterogeneous mixtures are listed. A mixture of sand and common salt is regarded as a heterogeneous mixture. No doubt, these are present in the same phase i.e., solid phase but have clear boundaries of separation. The particles of sand and common salt can be easily seen in the mixture.
(b) A saturated solution can be made unsaturated in two ways :
- By increasing the temperature or by heating
- By adding more of the solvent or by diluting the solution.
Question 18.
- Name a non-metallic element found in
- liquid state
- gaseous state.
- Pick metalloid from the elements carbon, silicon, phophorus, gold.
- Which two properties of metals enable us to give the desired shapes to metals ?
Answer:
-
- Bromine (Br2)
- Oxygen (O2).
- Silicon (Si) is a metalloid.
- Metals are melleable and ductile, i.e. they can be beaten into sheets and drawn into wires.
Question 19.
Why does a salt disappear when dissolved in water ?
Answer:
Water helps in separating ions from a salt. This inter-ionic forces decreases and the ions gets dispersed. Therefore salt dissolved in water and disappears.
Question 20.
(a) Name a metal which is liquid at room temperature.
(b) Smoke and fog are aerosols. How do they differ from each other?
(c) Name an element which melts when kept on the palm.
Answer:
(a) Metal is mercury(Hg)
(b) In smoke, dispersed phase is a solid (dust or carbon particles). In aerosols, it is a liquid (water drops). Dispersion medium in both the cases is the same i.e. air.
(c) It is either gallium (Ga) or cesium (Cs).
Question 21.
- Name a metal which is the best conductor of heat.
- Among the substances given below choose the elements, mixture and compound.
- Air
- Lead
- Diamond
- Calcium carbonate.
Answer:
- The metal is silver(Ag).
- Air (Mixture)
- Lead (Element)
- Diamond (Element)
- Calcium carbonate (Compound).
Question 22.
(a) Draw a flow sheet diagram to show the process of obtaining constituent gases from air.
(b) Which gas condenses first ? Why ?
Answer:
(a)
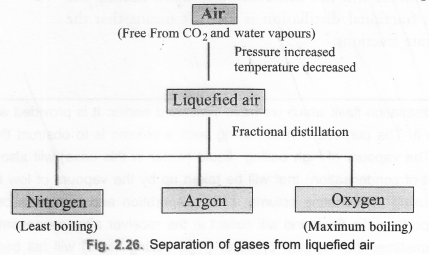
(b) Nitrogen (N2) condenses first because its boiling point is the least (-196°C) among all the gases present in air.
Question 23.
Name the appropriate methods for the separation of the following :
- nitrogen from air
- dye from blue ink
- cream from milk
- ammonium chloride from common salt.
Answer:
- Nitrogen is one of the constituents of air. It can be separated with the help of fractional distillation,
- Chromatography helps in separating dye from blue ink.
- Centrifugation or churning helps in separating cream from milk.
- Ammonium chloride is of volatile nature while common salt (sodium chloride) is not. The separation can be done with the help of sublimation.
Question 24.
(a) Identify the solute and solvent in tincture of iodine.
(b) Why is Tyndall effect not seen in a true solution ?
Answer:
(a) In tincture of iodine; solute present is iodine and solvent is ethyl alcohol.
(b) In a true solution, the particle size is so small that it does not scatter the beam of light. Therefore,
Tyndall effect is not seen in a true solution.
Question 25.
- Arrange solids, liquids and gases in increasing order of the following properties of matter
- rigidity
- diffusion
- compressibility.
- Write one example from your daily life which is based on diffusion of gases.
Answer:
-
- Rigidity : Gases < Liquids < Solids
- Diffusion : Solids < liquids < gases
- Compressibility : Gases < Liquids < Solids
- Smell of aroma or perfume released in one corner of the room soon spreads throughout.
Question 26.
What is a saturated solution ? What happens when a saturated solution is heated ?
Answer:
A solution is said to be saturated if no more of a solute can dissolve in it at a given temperature.
A saturated solution becomes unsaturated upon heating.
Question 27.
- Colloidal solutions show Tyndall effect but true solutions do not. Discuss.
- Explain how does soap help in cleaning dirty clothes ?
Answer:
- In a colloidal solution, the particle size is such (1 nm to 100 nm), that these particles scatter the light rays as they fall on them. Because of scattering, the path of the light as well as the particles become visible. But in a true solution, the particle size is so small (less than 1 nm) that these particles are not in a position to scatter the light. Therefore, true solution does not show any Tyndall effect.
- In dirty clothes, the dust particles are sticking on the oil drops present. Simple water cannot remove these oil drops from the clothes because water and oil as such do not form a stable emulsion. Soap plays the role of emulsifier and helps in forming a stable emulsion between the two. In other words, it helps in mixing oil and water. This means that soap helps in removing these oil drops along with the dirt sticking to them. The dirty clothes get washed by soap solution.
Class 9 Science Chapter 2
Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
- Fog and cloud are both colloidal in nature. How do they differ ?
- What is the function of fractionating column in fractional distillation ?
Answer:
- Both fog and cloud are the examples in which liquid (water) is the dispersed phase and gas (air) is the dispersion medium. The only difference between them is that clouds are formed in the upper atmosphere while fog gets formed in the region close to earth.
- A fractionating column obstructs the upwards movement of the vapours of the liquids. As a result, the energy (latent heat of condensation) which is released by the high boiling liquid is taken by the low boiling liquid. It remains in the vapour state. The high boiling liquid by releasing energy condenses and falls back in the distillation flask. Thus, fractionating column helps in the separation of the components from a liquid mixture. For example, a mixture of ethyl alcohol and water.
Question 2.
- Can we separate a mixture of water and alcohol by the use of a separating funnel ? If not, suggest a suitable method.
- You are provided with two liquids, one is a mixture of two miscible liquids while the other is a pure compound. Suggest two ways to distinguish them from each other.
Answer:
- No, it is not possible because water and alcohol form a miscible liquid mixture. The separation can be done with the help of fractional distillation. Alcohol (ethyl alcohol) with lesser boiling point distills leaving behind water in the distillation flask.
- The distinction can be made as follows :
- In case the constituents of a given liquid can be separated by methods like simple distillation or fractional distillation, it is a liquid mixture. If it is not possible, then the liquid is a compound.
- Find the boiling points of both the liquids. In case it is sharp, the given liquid is a compound. In case it is not, then the given liquid is a mixture.
Question 3.
Classify the following as physical and chemical changes. Give reason for your answer.
- Burning of candle.
- Melting of ice.
- Burning of petrol in an engine.
- Change of colour of iron bar on strong heating.
- Churning of milk to get butter.
Answer:
- Chemical change : The way present in the candle changes to liquid state. This means that the change is of physical nature. At the same time, the constituents carbon and hydrogen present in wax react with oxygen of air to form new substances. This means that a chemical reaction or change is also taking place.
- Physical change : When water formed as a result of melting of ice is cooled to 0°C, it changes back to ice.
- Chemical change : Petrol is a mixture of different hydrocarbons. They undergo oxidation or combustion upon burning to form carbon dioxide and water vapours along with heat energy. Therefore, it is a chemical change.
- Physical change : Iron bar regains its colour on cooling.
- Physical change : There is only a change of physical state and no new substance is formed.
Question 4.
Give an example of a mixture which exhibits the following characteristics.
- Two non-miscible components.
- Two volatile components differing in boiling points by more than 30°C.
- Two coloured components.
- Water containing a soluble salt.
- Volatile and non-volatile solid components.
Suggest a suitable method for separating constituents in each case.
Answer:
- Carbon disulphide and water. The separation can be done by a separating funnel.
- Ethyl alcohol and ether. The separation can be done by simple distillation. However, proper precaution must be taken since ether vapours catch fire.
- A mixture of blue-black ink. Separation can be done by chromatography.
- A mixture of copper sulphate and water. The separation can be done by concentration followed by cooling the concentrated solution (crystallisation).
- A mixture of naphthalene and sodium chloride. Separation can be done in a china dish, covered by a funnel. The process is called sublimation. Naphthalene gets separated as sublimate leaving behind sodium chloride.
Question 5.
You are provided with a mixture containing iron filings, ammonium chloride, sand and sodium chloride. Describe the procedure that you would use to separate the constituents from the mixture.
Answer:
Place the mixture on a paper or petridish. Move a bar magnet a number of times over the mixture. Iron filings get attached to the magnet and can be separated later on by scrapping. Transfer the remaining mixture to a china dish and subject it to the sublimation process. Ammonium chloride sublimes leaving behind sodium chloride and sand. Transfer the mixture to a glass beaker. Add a small amount of water and stir with a glass rod for some time. Sodium chloride completely dissolves in water leaving behind sand as such. The latter can be removed by filtration. The filtrate on concentration and cooling gives crystals of sodium chloride.
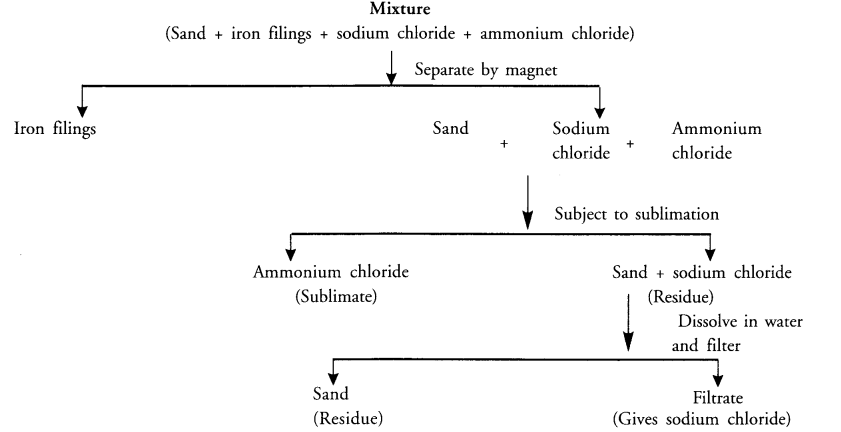
Question 6.
Process of simple distillation can be used to separate the constituents from a liquid mixture differing in their boiling points by 25°C or more. However, fractional distillation is effective if the difference in boiling points is less than 25°C. How will you explain this ?
Answer:
In simple distillation, only the low boiling liquid will distil while high boiling liquid will remain in the distillation flask. Thus, separation can be done if the difference in the boiling points of the liquids is 25° C or more. In the second case, both the liquids will distil simultaneously. The distillate will contain the fractions of both the liquids. If a fractionating column is used, the vapours of high boiling liquid will also rise into the column along with the low boiling liquid. But they will condense first releasing energy (called latent heat of condensation) and fall back in the distillation flask as a liquid. This energy will be absorbed by the vapours of the low boiling liquid which will remain in the vapour state. It will get distilled while the high boiling liquid unable to get distilled, will remain in the distillation flask only. In this way, separation can be done. Thus, the role of fractionating column is to put obstructions in the path of the vapours of the liquids that are rising upwards.
Question 7.
Give an example of a mixture which exhibits following characteristics.
- Two non-miscible components,
- Two volatile components with appreciable difference in boiling points.
- Two coloured components.
- Water containing certain suspended particles.
- Water containing a soluble salt. (f) A volatile and a non-volatile component.
Answer:
- A mixture of kerosene and water.
- A mixture of ether (b.p. = 35° C), and ethyl alcohol (b.p. = 78° C).
- A mixture of blue/black ink.
- A colloidal solution of starch.
- A mixture of copper sulphate in water.
- A mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium chloride.
Question 8.
Rama tested the solubility of four substances at different temperatures and found in grams of each substance dissolved in 100 g of water to form a saturated solution.
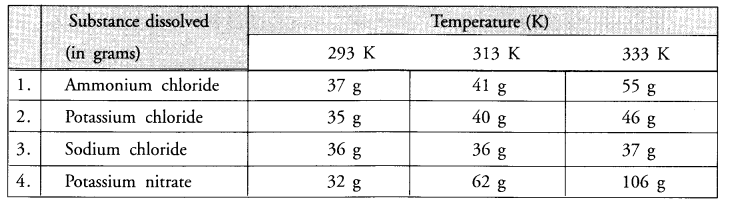
- Which substance is least soluble at 293 K.
- Which substance shows maximum change in its solubility when the temperature is raised from 293 K to 313 K ?
- Find the amount of ammonium chloride that will separate out when 55 g of its solution at 333 K is cooled to 293 K.
- What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a salt ? –
- What mass of sodium chloride would be needed to make a saturated solution in 10 g of water at 293 K ?
Answer:
- Potassium nitrate is least soluble in water at 293 K.
- Potassium nitrate shows maximum change in its solubility which is 30 g (62-32) per 100 g of water.
- From the available information, 55 g of ammonium chloride solution upon cooling from 333 K to 293 K separates salt = (55 – 37) = 18 g.
- From the available information, it is clear that the solubility of salt in water increases with the rise in temperature.
- At 293 K, in a saturated solution,
100 g of water has sodium chloride = 36 g
10 g of water has sodium chloride = 3.6 g
Question 9.
- Name the separation technique used to separate the constituents of the mixture of miscible liquids. Draw a labelled diagram of the process for separating mixture of acetone and water.
- List two properties of the mixture of miscible liquids essential for the process.
- K simple fractionating column is provided with beads. Give reasons.
Answer:
- The separation technique depends upon the boiling temperature difference between the miscible liquids.
If they differ in their boiling points by 25°C or more, the separation can be done by simple distillation. If the difference is less than 25°C, fractional distillation is used. Acetone (b.p. = 56°C) and water (b.p. = 100°C) can be separated by simple distillation. For the labelled diagram,
- The constituents of the miscible liquids should be volatile in nature.
The constituents of the miscible liquids should not react chemically with each other. - The purpose of beads in the fractionating column is to obstruct the upward movement of liquid with higher boiling point. This helps in the separation of the two liquids.
Question 10.
The concentration of a salt solution in terms of mass by mass percentage is 20% and the mass of the solution is 550 g. Determine the mass of solute present in the solution.
Answer:
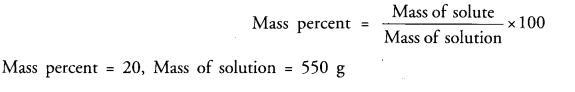
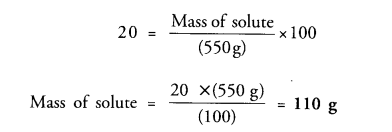
Question 11.
(a) To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find the concentration at this temperature.
(b) What is the effect of temperature on the solubility of a solid in a liquid ?
(c) Why is it possible to distinguish the particles of a solute from those of a solvent in a suspension ?
Answer:
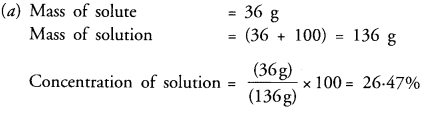
(b) Solubility of a solid in a liquid is generally directly proportional to the temperature. If the temperature increases, the solubility increases. If the temperature decreases, so is the solubility. However, there are some exceptions also. Solubility of lithium carbonate in water decreases with increase in temperature.
(c) In a suspension, the size of the particles of the dispersed phase is quite big. They can be easily distinguished from the particles of the dispersion medium. They can be seen even with naked eye.
